Nail fungus (onychomycosis) of the legs is a disease that develops as a result of damage to nail plaques with mushrooms with dermatophytes (up to 96%), more frequent molds and yeast (about 4%).The infection most often spreads from the skin of the feet with a long existing mycosis on the legs.Here he finds favorable conditions for development - increased humidity and nutrients.Under the influence of pathogens, the structure is impaired and the color of the nails changes.Over time, their complete destruction occurs.
Onychomycosis is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a serious illness that is subjected to timely detection and adequate treatment under the supervision of a dermatologist.
The fungus of the legs are recorded in millions of people around the world.About 5% of the total population suffer from onychomycosis.The wisest disease is common in people from 50 - 60 years.Every second person is ill in this age group.The treatment of their pathology is difficult due to the presence of somatic pathology, mainly vascular and endocrine.Men are sick more than women.Older people become more ill than young people.Children rarely suffer, mainly suffering from serious illnesses.In AIDS, the disease has an atypical picture.
The causative agents of onychomycosis
The cause of onychomycosis of the legs is different types of mushrooms: dermatophytes, yeast or mushroom mushrooms separately or in combination.
- Dermatophytes of mushrooms represent up to 90% of all onychomycosis.They are represented by mushrooms of the genus Trichophyton (most often T. Rubrum and T.Mentagrophytes var. Interdigitale).Most often, the leg slabs are affected by the trichopitone rubric.Dermatophytes are common in moderate climate countries.
- Candida onhomycosis fungus, as well as legs, rarely cause.They represent about 3% of all onychomycosis.In addition to Candida albicans, mushrooms such as S. tropicalis, S. parapsilosis and S. guilliermondii also cause the disease.
- Most mold mushrooms are not able to cause nail fungus themselves.Only a few of their species are independent pathogens - these are Scytalidium hyalinum and S. dimidiatum (Nattrassia magniferee), which are no more pathogenic with dermatophytes.The onychomycosis of the legs is such forms as scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Aspergillus spp., Pyrenochaeta unguis-heominis, alternaria sp., Fusarium spp.et al.The infection is most common in countries with hot and humid climates - tropics and subtropics.
Epidemiology of the disease
Most of the onychomycosis is an anthropophilic infection.They are sick and spread infection mainly people.
Dermatophyte mushrooms
The tank and source of dermatophytic mushrooms are a sick person whose pathogens are transmitted with direct contact or his or her personal belongings.The infection almost always extends to the toenails with the affected legs, the disease of which is clear and secret (deleted forms of mycosis).The risk of infection increases many times in the presence of a disease in one of the family members.
Mushrooms are transmitted through infected shoes, clothes, files and nail beans, carpet, linen, cloth, towel and more.The transmission of the infection occurs when the common bath, in the shower, sauna, pool, fitness hall and on the beaches.It contributes to the entry of mushrooms into the legs by walking barefoot in common parts.Pathogens live a long time on wooden floors and floor.
Yeast -like mushrooms
Candida -like mushrooms, like Candida, are saprophytic flora and always live on a person's skin.The good immune system is limited by the growth of pathogens.Prolonged administration of antibiotics, contraceptives, glucocorticoids and cytostatics, endocrine pathology (often diabetes mellitus) and a number of diseases that exhaust the immune system.Explosive mushrooms penetrate the nails from the skin and mucous membranes of the patient himself or enter the human body with infected products rich in carbohydrates.
Forms
The little ones live in the soil.Their disputes come across products, things and objects of the environment.Nedimatophytes do not spread to people.
Risk factors for the development of the disease
For mushrooms, dermatophytes are characterized by hereditary predisposition, male, age in the elderly, vascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, conditions of immunodeficiency, increased sweating, nail injury and other dermatomycosis.
The infection of yeast -like mushrooms such as Candida is characterized by fever and humidity, conditions of immunodeficiency, increased blood glucose, nail injury and non -compliance with personal hygiene rules.
Mushroom mushroom infection is characterized by severe immunodeficiency conditions and nail injury.
Groups of risk
The risk group for the development of onychomycosis includes:
- Persons who constantly use changing rooms, showers, saunas and more.
- Professional athletes (swimmers, football players, athletes, etc.).
- Military officials and other groups of people who use their own shoes.
- Male faces.
- Age older than 60 years.
Contribute to the development of leg fungus:
- Wearing tight, tightly adjacent shoes.
- Increased sweating or dry legs.
- Injuries and abrasions of the toenails, legs of the legs, roasted nails, etc.
- Accommodation in a humid and hot climate.
- Walking barefoot in public places.
- The presence of skin diseases in which keratinization of nails (psoriasis, ichthyosis) is impaired.
- Diseases such as diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency conditions, blood disorders of the lower limbs, blood disease, prolonged administration of corticosteroids, antibiotics and cytostatics.
- Genetic predisposition.
Fleet fungus development paths
There are several ways to penetrate mushrooms in the nails:
- Distal or distal-side (from free or lateral edge).
- Surface (directly through the nails).
- Proximal (supply -gut).
Distal-Lateral Mushroom Penetration Road
The distal or distal penetration pathway is characteristic of the mushrooms of Trichophyton Rubrum.Pathogens are introduced into the nail plate from the free edge (distal) or lateral areas (lateral edge).The main inflammatory process takes place in the nails, where increased cell proliferation occurs.The stepping layer of the skin of the free edge thickens (hyperkeratosis), resulting in the nails lifted and exfoliated (onycholysis).
In addition, the infection spreads in the direction of the hole and penetrates into the nails, which gradually (slowly) is destroyed.With damage to the matrix, a common dystrophic onychomycosis occurs.
Nail hyperkeratosis is observed in chronic eczema, psoriasis, warts, red flat lichen.
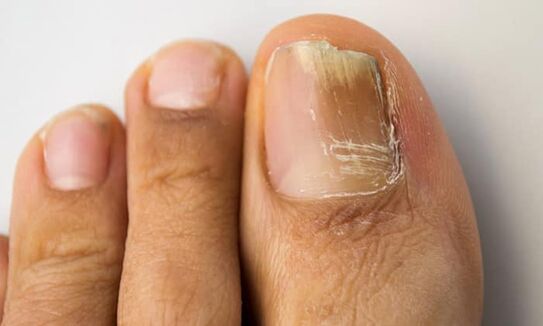
A surface path of mushroom spread
Mushroom Mentagrophytes var.Interdigitale is more aggressive in terms of excited nail structures than other dermatophytes.They mainly affect the outer part of the nails, causing the development of onychomycosis on the white surface.The mushrooms under the enzymes of keratinase perforate the layer of the layer with hyphons, gradually capturing all layers of the nails.1 and 5 fingers are affected.They are the subject of the largest trauma of the shoes when walking.The disease is affected by 1 and 4 intercostal folds.
It is believed that the superficial form of onychomycosis can also be caused by fungi-no-humanatophytes: acremonium spp., Fusarium oxysporum and some species aspergillus.
Proximal path to mushroom distribution
There is a third time of mushroom penetration into the nails - through a proximal nail roller and a nail bed.The lesion begins with the skin in the area of the nail roller, which thickens and exfoliates from the surface of the nail.In addition, the last part of the matrix and nail bed are involved in the process, with damage on which grooves, irregularities and cracks appear on the nail.With the penetration of pathogens into the nails, the nail acquires a white opaque color over time.Over time, complete destruction and loss of nails is noted.It is more common in HIV-infected patients with the spread of infection through blood vessels.
Mushroom damage characteristics similar to yeast
Damage to Candida mushrooms begins with paronychia - inflammation of the proximal (located near the hole).Its swelling and thickening are noticeable, which leads to the separation of the cuticle from the surface of the plate.In addition, mushrooms fall freely into the matrix and nails, causing, causing the nail from the tissues of the finger over time.
Mushroom damage characteristics by included
Damage to the nails of the mushrooms with non -heroophytes is secondary.Cheats (often scytalidium spp.), Placed in the already affected nails - cracks, space between nail combs or empty vessels.Then hyperkeratosis develops and slow nail destruction.
Clinical forms of onychomycosis of the legs
There are several forms of onychomycosis on the legs:
- Distal-laterage.
- White surface.
- Proximal.
- General dystrophic.
Distal-side submarine onychomycosis of the legs
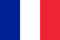
This form of the disease is the most common.In most cases, the cause of onychomycosis is dermatomycetes, in particular the trichopitone rublerum.Pathogens penetrate the nail plate on the side of the free edge and the lateral edges.Perenophaeum hyperkeratosis develops, resulting in a detachment of the nail from the tissues of the finger (onycholysis), it loses transparency, acquires a whitish or yellow color, begins to decay.With the development of hyperkeratosis of the submarine, the nail plate looks thickened.With the progression of the disease, the focus of the lesion expands to the hole, as indicated by the emerging stripes of yellow.Over time, the entire nails and matrix are involved in the pathological process, which over time leads to dystrophy and destruction of the nail.
In the elderly, there is a pronounced hyperkeratosis (thickening), onychgrifosis (thickening and deformity in the form of poultry) or Boykovichi (indentation deformity) is often observed.Their nails are often affected by mixed flora - dermatophytes, molds and even bacteria.
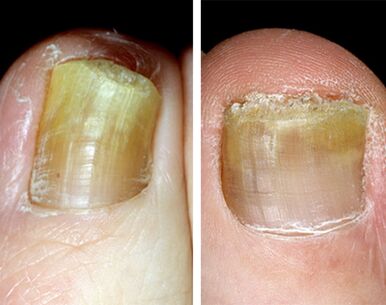
A surface (white) form of onychomycosis of the legs
The onychomycosis of the white surface of the legs is the second largest form of spread of damage.Its reason is mainly Trichophyton Mentagrophytes var.Interdigitale, which penetrates into the nail plate directly through its upper (pre-rsal) part, as well as some types of fungi-without hectophytes.Strongly affected by the nail of the first toe, rarely -the fifth.
At the beginning of their surface, small white spots and strips appear, which ultimately conquers a growing surface.Gradually the color turns yellow, ocher.The surface of the nail becomes loose, rough, powder, easily bounces.The thickening and separation from the nails does not appear.
The proximal submarine of onychomycosis of the legs
This form of mycosis is rare.It represents about 3% of all onychomycosis.The reason is the mushrooms similar to the yeast of Candida Albicans and Trichophyton Rubrum.Nail candidiasis is preceded by inflammation of the periodological roller.It swells, acquires red, becomes brilliant.The cortex rises and the infection penetrates into the end of the matrix and nails, when damaged by the groove, irregularities and cracks of the nails, there is a loss of natural shine and blurring.Gradually the nail is destroyed, in severe cases it disappears.This form of onychomycosis of the legs is often found in patients infected with HIV.
General dystrophic form of onychomycosis of the legs
This form of onychomycosis is more commonly developed with a long -term current (chronic course) disease, the cause of which is more often the fungi of the trichopitone river and Candida Albicans.At the same time, nails, bed and matrix are involved in the pathological process.The apology of the nail occurs as a result of the development of a submarine hyperkeratosis.Over time, the nails are destroyed and the new one due to the affected matrix does not grow or grow badly.
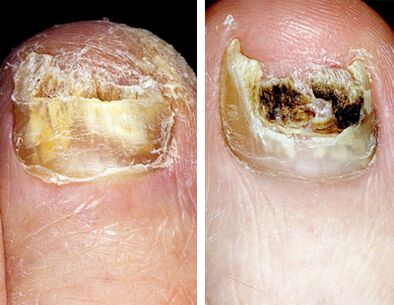
Types of damage to nail plates
There are 3 options for onychomycosis:
- Normorophic.
- Hypertrophic.
- Atrophic.
Normotrophic type of onychomycosis of the legs
With normotrophic type, the infection is localized in the upper layers of the nails.Its thickness and color in the disease do not change, but spots and stripes are visible in the depths.The color of the nails varies from white to deep yellow.After a while, spots and stripes merge.The damage zone spreads throughout the nails of the nails, except for the moon.No fracture and shrinkage are observed.Sometimes a slight loosening of the free edge is noted.Adequate treatment is possible for treatment.
Hypertrophic type of onychomycosis of the legs
This type of onychomycosis is the most common.As a result of the development of submarine hyperkeratosis, the nails are significantly thickened, deformed and loses its luster.The nails become uneven, dumb, they get a brownish-gray color and they fall apart.The Moon area is not affected.The disease gives the patient a tangible discomfort.In elderly patients, the development of onychgrifosis is noted - the nails thicken, lengthen and bend like a bird's nail.
Atrophic type of onychomycosis of the legs
With an atrophic (onycholithic) nail plate, it quickly loses its nail bond, many gaps appear in its layers, fades, becomes thinner and changes color to whitish or yellow-white.The surface remains smooth for a long time.Over time, partial destruction occurs.
Signs and symptoms of nail fungus
Most often, the change in the nail begins with a free (distal) or lateral (lateral) edge.
Changing color.With onychomycosis, a change in nail color is the first sign of the disease.It becomes opaque, often loses its luster, acquires white or yellow, with mushrooms overlap - brown, brown, green and even black.
Thickening.Increasing the number of excited masses as a result of the development of a submarine hyperkeratosis leads to thickening of the nail.
Lubrication and destruction.In the case of a disease as a result of the vital activity of the mushrooms, the nails first disintegrate and over time completely destroyed.
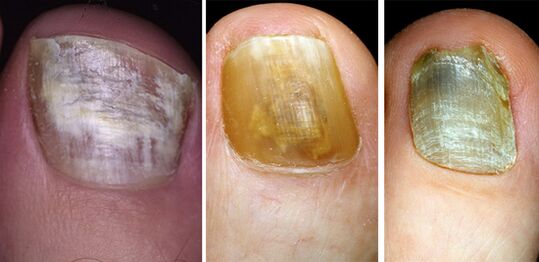
Nail damage characteristics with different types of onychomycosis
Nail damage to different types of fungal diseases has its own characteristics.The main types of pathogens are Trichophyton Rubrum (70 - 90%) and Trichophyton Mentagrophytes v.interdigitale (8 - 30%).Candida albicans, mushrooms of molds, T. Mentagrophytes V.Gypseum, T. Verrucosum, T. Tonsuras and T. Violaceum, Epidermophyton Floccosum, Trichophyton are much less common.Schonleinii.
Onychomycosis of the legs with Ribrofitia
The Ribrofits in the Russian Federation represent 70 to 90% of all mycoses.The legs in the disease are most commonly affected (usually flat-dry type).An indispensable satellite of Ribrofitia of the legs is a fungus of the toenails.In mycosis, the distal-diplutal form of onychomycosis usually develops, the pronounced hyperkeratosis is characteristic, several toes of the legs are affected at once and often toes on the one hand.The disease goes without special subjective sensations.The soreness and discomfort of wearing shoes occurs with pronounced hyperkeratosis, onychgrifosis and a nail.The source of infection is often in the patient's family.
Related onychomycoses are often recorded: Rubrum and Candida Albicans Trichophyton, Rubrum Trichophyton and Molds.It is important to evaluate cultural research.
Onychomycosis of the feet with T. Mentagofit Mushrooms.V.interdigitale
Mushrooms T. Mentagofits.V.interdigitale affect the skin of the feet and nails.Epidermophitosis represents 10 to 30% of the entire mycosis of the legs.
The disease is affected by the upper (dorsal) part of the nails.The superficial white form of onychomycosis usually develops.The pathological process is mainly involved in 1 and 5 toes (they are the subject of the largest trauma on shoes during walking) and 1 and 4 interpolars.The transmission of infection occurs with the use of a shared bathroom, in the shower, sauna, pool, beaches and pools.
Onychomycosis of the feet with disadvantage of yeast -like yeast, of the genus Candida
This form of leg mycosis is rare.It represents less than 3% of all onychomycosis.Often the disease is recorded in people with chronic generalized candidiasis.Nail damage, as a rule, begins with inflammation of the roller of the period, located near the hole.Its swelling and thickening are noticeable, which leads to the separation of the cuticle from the surface of the plate.In addition, the mushrooms fall freely into the matrix and nails (proximal form of underwater), if the nail appears channels, irregularities and cracks, there is a loss of natural shine and blurring, a brown-brown color manifests.Gradually the nail is destroyed, in severe cases it disappears.
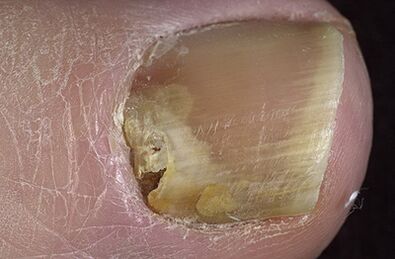
Onychomycosis of the legs caused by forms
Plastic mushrooms are inhabited in already affected nails - cracks, in the spaces between nails or empty vessels.Next, hyperkeratosis develops and slow nail destruction, which during the disease is colored in black (scytalidium spp.) Or green or gray (scopulariopsis brevicaulis) color.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis
The diagnosis of onychomycosis is based on data from an epidemiological history, a clinical picture of the disease and the data of the method of laboratory tests.
In a microscopic examination of the material, the nature of the disease (fungi or other pathogen) is established.The identification of mushrooms has been established by a microbiological examination (cultures of material on the nutrient medium) with the subsequent microscopy of pure culture.The process is laborious, success is achieved in half of the cases.Proper collection of materials from the affected nails is the key to a successful microbiological study.
Differential diagnosis
Only in half of the cases of patients with dermatologists with changes in the shape and color of the nails make fungal diseases.Onychomycosis should be distinguished from eczema, psoriasis, reactor syndrome, paccionihia, Daria disease, flat lichen, Norwegian scabies, bacterial lesions.